Over the world, millions of individuals suffer with diabetes. It is a chronic disease that impacts the way your body processes blood sugar (glucose), which is vital for your health. Glucose is an essential source of energy for the cells that make up your muscles and other tissues. It’s also the brain’s main source of fuel. However, having too much glucose in your blood can lead to various health issues. This simple guide aims to shed light on the types of diabetes, their symptoms, and basic management strategies.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is primarily divided into three categories: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational Diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes
This type is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Insulin must be taken daily by people with Type 1 diabetes in order to survive. It usually develops in children or young adults but can occur at any age.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is more common and usually develops in people over age 45, but increasingly, younger adults, teens, and even children are being diagnosed. In this scenario, the body doesn’t use insulin properly (known as insulin resistance), and over time, the pancreas cannot make enough insulin to keep blood glucose levels normal. Weight, lifestyle, and genetic factors play a significant role in Type 2 diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes
This type occurs in pregnant women who have never had diabetes but have high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. It affects both the mother and the baby’s health but usually resolves after giving birth.
Symptoms of Diabetes
The warning signs of diabetes can be so mild that you might not even notice them. These consist of intense hunger, weariness, increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s vital to consult a healthcare provider.
Managing Diabetes
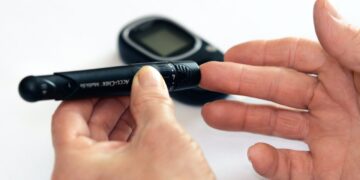
While there is no cure for diabetes, it can be managed with lifestyle changes and medication. Eating a healthy, balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, regular physical activity, and monitoring blood sugar levels are critical. For those with Type 1 diabetes, taking insulin is essential. People with Type 2 diabetes may need medication, lifestyle changes, or insulin to manage their condition.
Understanding diabetes is the first step towards managing it effectively. If you or someone you know is showing symptoms of diabetes, it’s important to see a healthcare provider. With the right support and management plan, people with diabetes can lead healthy, active lives.